Introduction
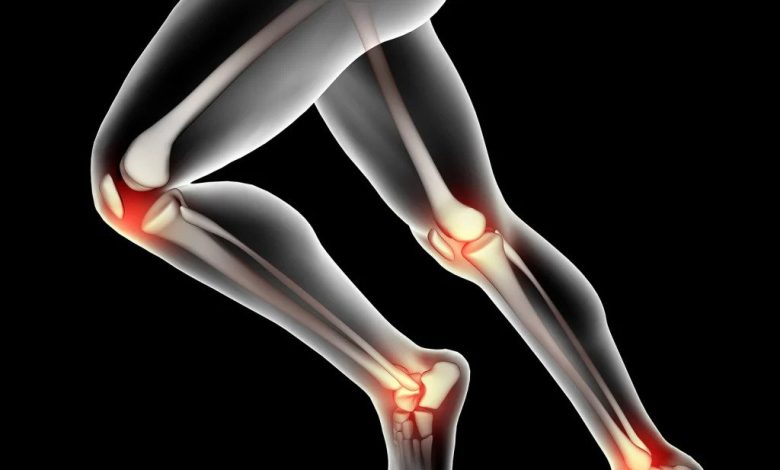
Osteoarthritis Treatment: Osteoarthritis, commonly referred to as OA, is a chronic degenerative joint condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by the progressive breakdown of cartilage in the joints, OA leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It predominantly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, and its prevalence is on the rise, primarily due to an aging population and lifestyle factors.
While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, numerous treatment options are available to help manage its symptoms, improve the quality of life, and delay disease progression. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the multifaceted world of osteoarthritis treatment, covering everything from non-pharmacological interventions to surgical solutions.
Understanding Osteoarthritis
Before we explore the intricacies of OA treatment, it’s crucial to understand the basics of this condition.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the articular cartilage, the smooth tissue that covers the ends of bones. This cartilage allows for smooth and pain-free joint movement. In OA, this cartilage starts to break down, and the underlying bones can become exposed and rub against each other, leading to pain, inflammation, and reduced joint function.
Common Symptoms of Osteoarthritis:
1. Joint pain, especially after inactivity or overuse.
2. Stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of rest.
3. Decreased range of motion in the affected joint.
4. Swelling and tenderness in the joint.
5. The development of bone spurs, visible as bony growths near the joint.
6. Audible cracking or grating sounds when moving the joint.
While the exact cause of OA remains a subject of ongoing research, several risk factors contribute to its development, including age, genetics, joint injuries, and obesity.
Non-Pharmacological Osteoarthritis Treatment
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
a. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is paramount, as excess weight puts added stress on weight-bearing joints. Weight loss can significantly reduce pain and improve joint function.
b. Exercise: Regular physical activity can strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joint, improve joint stability, and reduce pain. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking are recommended.
c. Assistive Devices: Canes, braces, and orthotic devices can help alleviate pain and improve mobility.
d. Physical Therapy: Professional guidance from physical therapists can lead to the development of personalized exercise routines and joint protection techniques.
2. Dietary Supplements:
a. Glucosamine and Chondroitin: These supplements are believed to support cartilage health and alleviate pain in some individuals.
b. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil and specific nuts and seeds, omega-3 fatty acids possess anti-inflammatory properties that may reduce joint pain.
Pharmacological Osteoarthritis Treatment
1. Over-the-Counter Medications:
a. Acetaminophen: A pain reliever suitable for mild to moderate OA pain.
b. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Available in both over-the-counter and prescription forms, these medications reduce pain and inflammation. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen and naproxen.
2. Prescription Medications:
a. Topical Analgesics: Prescription-strength creams or patches provide localized pain relief.
b. Opioids: Reserved for severe cases, opioid medications may be prescribed but typically for short-term use due to the risk of addiction.
Intra-Articular Injections:
1. Corticosteroid Injections: These injections deliver potent anti-inflammatory medication directly into the joint, providing relief from pain and inflammation.
2. Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Designed to supplement the joint’s natural synovial fluid, these injections offer temporary pain relief.
Surgical Interventions
1. Arthroscopy: In cases of significant joint damage, arthroscopic surgery may be used to remove damaged tissue, bone spurs, or loose fragments from the joint.
2. Osteotomy: This procedure involves reshaping the bones to realign the joint and relieve pressure.
3. Joint Replacement Surgery:
a. Partial Joint Replacement: Replaces only the damaged portion of the joint, typically performed in the hip or knee.
b. Total Joint Replacement: Commonly performed for hips and knees, this procedure involves replacing the entire joint with an artificial implant.
Post-Treatment Care
Regardless of the chosen treatment approach, post-treatment care is critical for long-term success and symptom management. Here are some crucial aspects to consider:
1. Physical Therapy: Continuing with physical therapy exercises to maintain joint strength and flexibility is crucial.
2. Medication Management: It’s essential to adhere to the prescribed regimen for medications and monitor for any potential side effects.
3. Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight and adopting an exercise routine tailored to your condition can make a significant difference in your OA management.
4. Assistive Devices: If recommended, continue using assistive devices for support and comfort.
5. Regular Follow-Ups: Routine follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential for assessing your progress and making any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Emerging and Investigational Osteoarthritis Treatments
While the above treatment options have been the cornerstone of osteoarthritis management for years, ongoing research continues to uncover new therapies and approaches. Some emerging and investigational treatments include:
1. Stem Cell Therapy: Utilizing stem cells to regenerate damaged cartilage and reduce inflammation.
2. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Concentrated platelets are injected into the joint to stimulate tissue repair and reduce pain.
3. Disease-Modifying Osteoarthritis Drugs (DMOADs): These drugs aim to slow or halt the progression of OA and may offer hope for more effective long-term management.
4. Biologic Injections: Innovative biologic agents are being developed to target specific molecules that contribute to OA, potentially offering a more targeted approach to treatment.
Determining the Best Treatment Plan
The best treatment for osteoarthritis varies from person to person, as it depends on factors such as the joint affected, the severity of the condition, the individual’s age, and overall health. A healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan, taking into account these factors.
In addition to the standard treatments mentioned above, there are emerging and investigational therapies that hold promise for the future of osteoarthritis management. These include:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Using stem cells to regenerate damaged cartilage and reduce inflammation.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Concentrated platelets are injected into the joint to stimulate tissue repair and reduce pain.
- Disease-Modifying Osteoarthritis Drugs (DMOADs): These drugs aim to slow or halt the progression of OA and may offer hope for more effective long-term management.
- Biologic Injections: Innovative biologic agents are being developed to target specific molecules that contribute to OA, potentially offering a more targeted approach to treatment.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis is a common and potentially debilitating condition that affects millions of individuals. While it cannot be cured, a multitude of treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms, enhance the quality of life, and potentially slow disease progression. The most effective treatment plan often involves a combination of non-pharmacological approaches, medication, and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
It’s crucial for individuals with OA to work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor a treatment plan that suits their unique needs and circumstances. With the right treatment and diligent self-care, individuals with osteoarthritis can enjoy a better quality of life and maintain their mobility, even in the face of this challenging condition.